Polycarbonate is a remarkable thermoplastic known for its durability and versatility. This high-performance plastic is utilized across a multitude of industries, thanks to its unique properties. From safety equipment to automotive parts, polycarbonate serves as a reliable alternative to traditional materials like glass. Understanding polycarbonate not only highlights its importance in manufacturing and construction but also showcases its role in innovative applications. In a world where durability, safety, and efficiency are paramount, polycarbonate stands out as an ultimate choice for various products. This article delves into the characteristics, uses, and advantages of polycarbonate, providing a comprehensive view of this essential material.
What is Polycarbonate?
Polycarbonate is a type of plastic that belongs to the family of thermoplastics. It is made from a polymer composed of carbonate groups, which gives it unique properties. The material is characterized by its high impact resistance and optical clarity, making it suitable for applications where strength and visibility are critical. Polycarbonate is produced through a process called polymerization, where monomers combine to form long chains. This structure contributes to its toughness and flexibility. Additionally, polycarbonate can be molded into various shapes, allowing manufacturers to create a wide range of products. Its inherent properties make it a favorite in sectors such as construction, electronics, and automotive industries.
How Polycarbonate is Made
The manufacturing process of polycarbonate begins with the polymerization of bisphenol A (BPA) and phosgene. This chemical reaction produces a viscous liquid, which is then cooled and solidified into pellets or sheets. The raw materials are crucial for ensuring the final product’s quality, as they influence the physical and chemical properties of the polycarbonate. Once produced, the polycarbonate can be further processed through techniques like extrusion, injection molding, or thermoforming. These methods allow manufacturers to shape the material into various forms, from sheets to intricate components. The ability to customize polycarbonate’s thickness and transparency makes it an ultimate choice for diverse applications, meeting specific industry demands.
Key Properties of Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate possesses several key properties that contribute to its popularity. Firstly, it offers exceptional transparency, allowing up to 90% light transmission, which is comparable to glass. This feature makes it ideal for applications where visibility is essential, such as optical lenses and safety shields. Secondly, polycarbonate is highly impact-resistant, making it difficult to break or shatter, thus providing safety in environments where accidents can occur. Additionally, it has a high heat resistance, allowing it to withstand temperature variations without losing structural integrity. Moreover, polycarbonate can be treated for UV protection, preventing yellowing and degradation when exposed to sunlight. These properties collectively make polycarbonate a superior choice for many applications, combining safety, functionality, and aesthetic appeal.
Common Uses of Polycarbonate
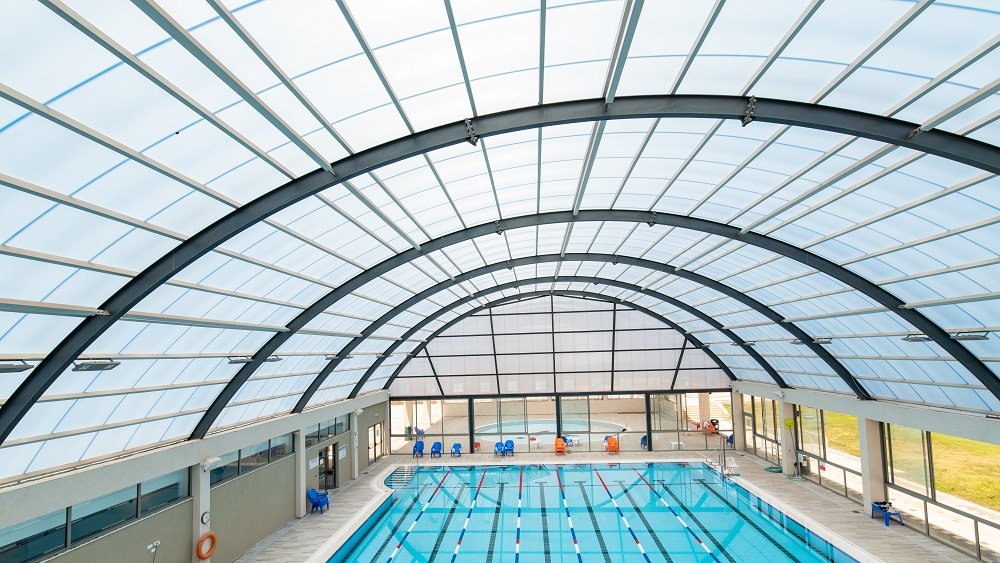
Polycarbonate is widely used in various industries due to its impressive characteristics. In construction and architecture, polycarbonate sheets are commonly employed as roofing materials, skylights, and glazing systems, providing excellent insulation while allowing natural light to enter. In the electronics sector, polycarbonate is utilized for manufacturing durable housings for devices, such as smartphones and laptops, due to its lightweight nature. The automotive industry also benefits from polycarbonate, using it for headlights, windows, and interior components, enhancing both safety and design. Additionally, polycarbonate is found in protective gear like face shields and safety goggles, where impact resistance is crucial. The versatility of polycarbonate ensures its presence in everyday products and specialized equipment alike.
Advantages of Using Polycarbonate
One of the primary advantages of Polycarbonate is its durability. Unlike glass, polycarbonate is shatter-resistant, making it an excellent choice for safety applications. Its lightweight nature reduces transportation costs and makes installation easier, especially in construction projects. Additionally, polycarbonate’s insulation properties contribute to energy efficiency, as it can help regulate temperatures in buildings. The material is also relatively easy to work with; it can be cut, drilled, and shaped without difficulty, allowing for creative applications. Furthermore, polycarbonate’s resistance to UV radiation ensures that products maintain their clarity and strength over time, reducing the need for replacements. These benefits make polycarbonate an ultimate choice for industries seeking reliable and efficient materials.
Disadvantages of Polycarbonate
While polycarbonate has many advantages, it also has some drawbacks. One significant concern is its susceptibility to scratching; although it’s impact-resistant, its surface can be easily marred without proper coatings. This can affect its optical clarity over time, particularly in applications where visibility is crucial. Additionally, polycarbonate can be more expensive than alternatives like acrylic or glass, which may deter budget-conscious projects. Another consideration is that certain grades of polycarbonate can warp under prolonged exposure to high temperatures, limiting its use in specific environments. Despite these disadvantages, many industries find that the benefits of polycarbonate often outweigh the drawbacks, especially when considering its unique properties and applications.
Comparing Polycarbonate with Other Materials
When comparing polycarbonate with other materials, such as glass and acrylic, several differences become apparent. Polycarbonate is significantly lighter than glass, making it easier to handle and install. While glass offers superior scratch resistance, polycarbonate outperforms it in terms of impact resistance. Acrylic, on the other hand, is lighter than both polycarbonate and glass but lacks the same level of durability. Polycarbonate is also better suited for outdoor applications due to its UV protection, while acrylic tends to yellow over time when exposed to sunlight. In terms of cost, polycarbonate is often more expensive than acrylic but can be more affordable than high-quality glass. Ultimately, the choice between these materials depends on specific application requirements and budget considerations.
Environmental Impact of Polycarbonate
The environmental impact of polycarbonate is an important consideration in today’s eco-conscious society. While polycarbonate itself is durable and long-lasting, its production process involves the use of petrochemicals, raising concerns about sustainability. However, many manufacturers are now exploring recycling options for polycarbonate products, promoting a circular economy. Polycarbonate can be recycled multiple times without significantly degrading its properties, making it a more sustainable option compared to some other plastics. Additionally, advancements in bioplastics may lead to the development of more environmentally friendly alternatives in the future. As industries continue to seek sustainable practices, understanding polycarbonate’s impact and exploring recycling opportunities is crucial for responsible material usage.
Conclusion
In conclusion, polycarbonate is a versatile and durable material that plays a significant role in various industries. Its unique properties, such as high impact resistance, optical clarity, and lightweight nature, make it an ultimate choice for applications ranging from construction to electronics. While there are some disadvantages, the overall benefits of polycarbonate, including its adaptability and safety features, often outweigh the concerns. As technology evolves, we can expect even more innovative applications for polycarbonate, further solidifying its importance in the material landscape. By understanding polycarbonate and its uses, we can appreciate its value in enhancing our daily lives and the products we rely on.